Paint / Film Adhesion Testing As per standard ASTM D 3359
Ensuring Coating Quality: A Guide to Paint and Film Adhesion Testing with ASTM D3359
Introduction
- Coatings such as paints and films play a vital role in enhancing the appearance, durability, and protection of surfaces. However, the effectiveness of these coatings largely depends on their adhesion to the substrate. Poor adhesion can lead to peeling, flaking, and premature failure, ultimately affecting the product's performance and lifespan. This is where ASTM D3359, the standard for paint and film adhesion testing, comes into play. In this blog post, we'll explore ASTM D3359, its testing methods, and its importance in ensuring coating quality.
What is ASTM D3359?
ASTM D3359 is a widely recognized standard for assessing the adhesion strength of paint and other coatings on a substrate using a tape test. This test method provides an easy-to-perform, fast way to check how well a coating is bonded to a surface, which is crucial for quality control in industries ranging from automotive to construction.
The standard consists of two test methods: Method A (X-cut) and Method B (Cross-cut). Each method is used depending on the type of coating and its thickness, allowing for flexibility in evaluating various coatings.
Why Adhesion Testing Matters
A coating’s adhesion directly impacts its ability to protect the underlying surface. If a coating fails to adhere properly, it can peel or flake off, exposing the substrate to environmental elements, corrosion, and wear. This not only compromises the appearance but can also lead to costly repairs or replacements. Proper adhesion testing helps:
- Ensure Durability: Confirms that coatings can withstand environmental and mechanical stresses.
- Improve Product Quality: Identifies potential adhesion issues early in the manufacturing process.
- Comply with Industry Standards: Meets quality benchmarks required in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The Two Test Methods in ASTM D3359
1. Method A: X-Cut Tape Test
This method involves cutting an X-shaped incision through the coating down to the substrate. Here’s how it’s typically conducted:
- Step 1: Using a sharp blade, make two intersecting cuts (forming an “X”) into the coating, ensuring the cuts penetrate to the substrate.
- Step 2: Firmly apply a piece of pressure-sensitive adhesive tape over the cut.
- Step 3: Smooth the tape to remove air bubbles and ensure good contact.
- Step 4: Remove the tape by pulling it back sharply at a consistent angle (usually 180 degrees).
- Step 5: Inspect the cut area to assess how much of the coating has been removed.
The adhesion is then evaluated based on the extent of the coating that has lifted from the substrate. This method is generally suitable for coatings thicker than 125 micrometers.
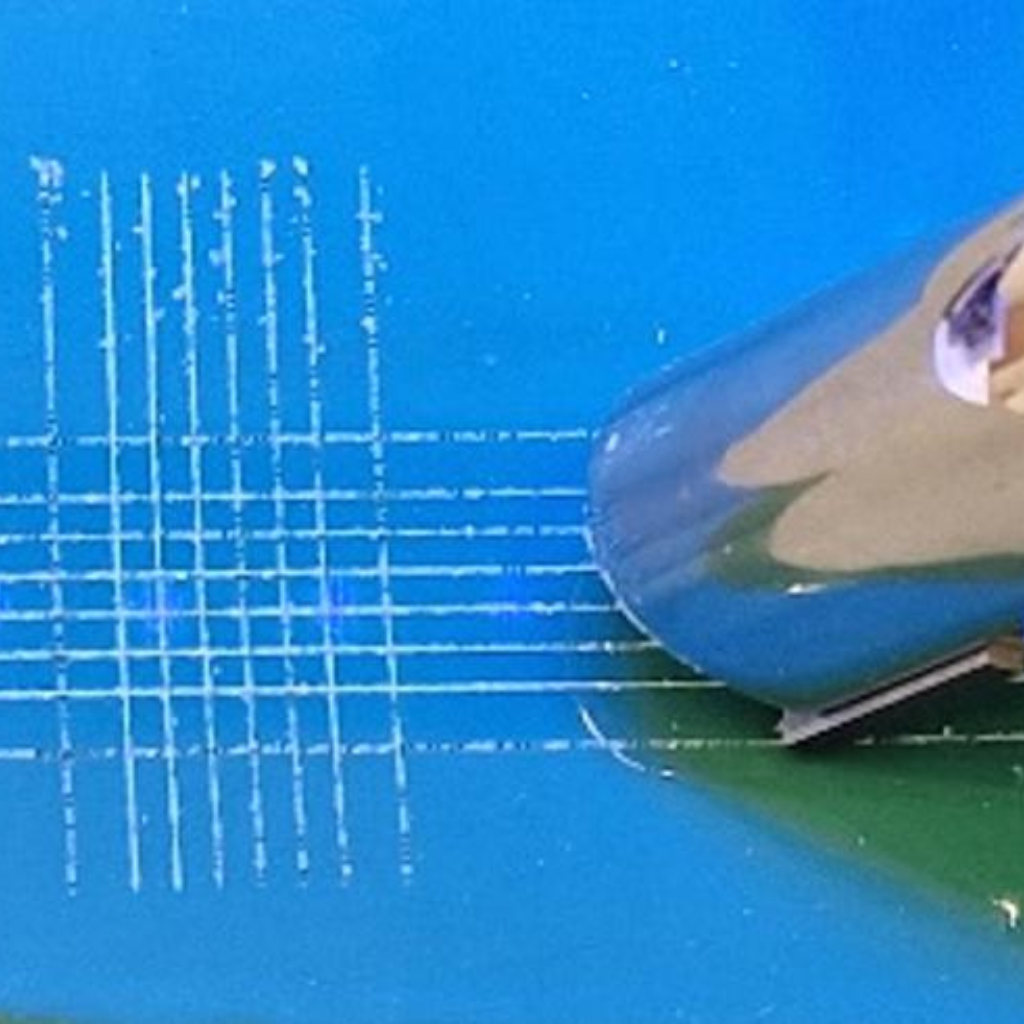
2. Method B: Cross-Cut Tape Test
The Cross-Cut Tape Test is ideal for coatings less than 125 micrometers thick and involves creating a grid-like pattern of cuts on the coating. Here’s how it’s performed:
- Step 1: Use a specialized cutting tool or blade to make a series of parallel cuts in the coating, penetrating down to the substrate.
- Step 2: Make another set of parallel cuts perpendicular to the first, forming a cross-hatch pattern (grid).
- Step 3: Apply a piece of pressure-sensitive tape over the cross-hatch pattern.
- Step 4: Smooth the tape to remove any air bubbles.
- Step 5: Remove the tape by pulling it back sharply at a consistent angle.
- Step 6: Inspect the grid area to determine the amount of coating that has been removed.
This method provides a rating from 0 to 5, with 5 indicating perfect adhesion (no coating removal) and 0 indicating poor adhesion (greater than 65% coating removal).
Interpreting the Results
- Method A (X-Cut Test): The test results are often qualitative, describing the amount of coating that has detached from the substrate. Terms like “excellent,” “good,” or “poor” adhesion are used to describe the results.
- Method B (Cross-Cut Test): The results are rated on a numerical scale from 0 to 5:
- 5: No peeling or removal of the coating.
- 4: Trace peeling or removal along the cuts.
- 3: Jagged removal along the cuts, up to 1.6 mm on either side.
- 2: Removal along most of the grid cuts, up to 3.2 mm on either side.
- 1: Significant removal between squares of the grid.
- 0: Complete or nearly complete removal over the grid.
These ratings help in comparing different coatings’ adhesion properties, ensuring the quality and durability of the finished product.
Applications of ASTM D3359
ASTM D3359 is widely used in various industries to ensure the quality and reliability of coated products:
- Automotive: Testing the paint adhesion on car bodies and components.
- Aerospace: Ensuring protective coatings on aircraft parts adhere properly.
- Construction: Evaluating the adhesion of paints on building materials to withstand weathering.
- Consumer Goods: Testing coatings on electronic devices, furniture, and appliances to maintain their appearance and protective features.
Benefits of Using ASTM D3359
- Quick and Cost-Effective: Provides a fast and affordable way to assess coating adhesion.
- Standardized: Offers a uniform method for evaluating coating adhesion, making results comparable across different applications.
- Quality Assurance: Helps manufacturers maintain high-quality standards, reducing the risk of product failures and customer complaints.
Limitations of ASTM D3359
While ASTM D3359 is an effective method for adhesion testing, it has its limitations:
- It is mainly qualitative and not suitable for thick or textured coatings.
- It may not fully represent the performance of coatings under extreme environmental conditions.
- The results can be influenced by factors such as tape selection, cutting tool sharpness, and user technique.

Conclusion
- ASTM D3359 is an essential standard for assessing the adhesion of paint and film coatings. By providing a simple, yet effective way to test adhesion strength, it ensures that coatings will perform reliably in their intended applications. For industries where coatings play a critical role in product performance, this test is invaluable for quality control and product development.

