Water Resistance Test As Per Standard MS 655-08
Ensuring Material Durability: Water Resistance Testing as per MS 655:08
Introduction
- In industries ranging from construction to electronics, the durability of materials in the presence of water is a key concern. Water resistance testing is a crucial process that helps determine whether a material can maintain its integrity and performance when exposed to water or high humidity. The Malaysian Standard MS 655:08 provides a rigorous framework for conducting these tests, ensuring consistency, reliability, and safety in material performance.
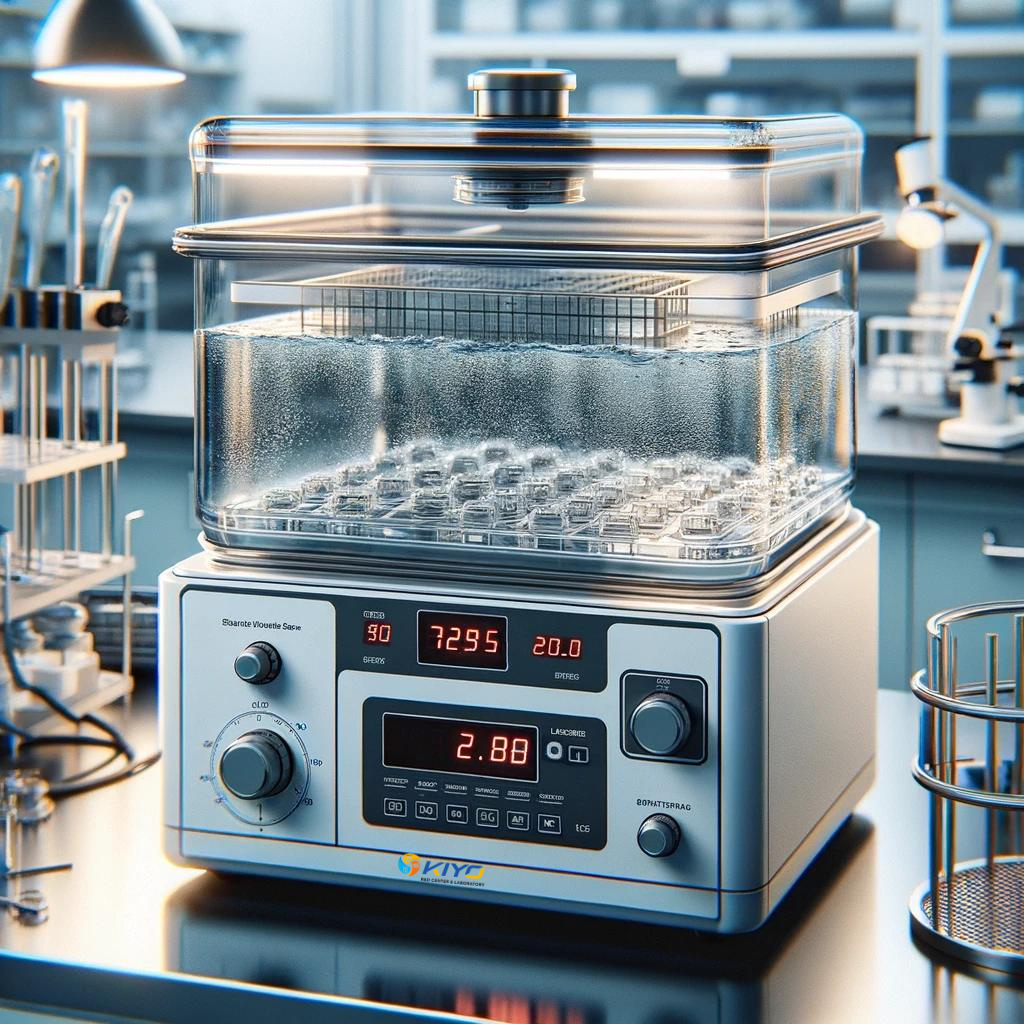

What Does MS 655:08 Cover?
MS 655:08 is a well-established standard that specifies the methods for testing the water resistance of various materials. It is widely recognized across multiple sectors where water exposure is a significant concern. Whether for materials used in buildings, vehicles, or consumer electronics, adhering to MS 655:08 helps ensure that products meet necessary durability standards.
The standard outlines precise procedures for evaluating how materials react to different forms of water exposure, such as direct immersion, spraying, or high humidity environments. It also specifies the criteria for acceptable performance, ensuring that materials that pass these tests can be reliably used in water-prone conditions.
The Importance of Water Resistance Testing
Water resistance testing is vital for several reasons:
- Product Longevity: Materials that fail to resist water effectively can degrade over time, leading to reduced product lifespan. Water resistance testing helps manufacturers ensure their materials can endure long-term exposure without deteriorating.
- Safety Compliance: For many products, especially those involving electronics or construction materials, inadequate water resistance can lead to safety hazards. Testing to the MS 655:08 standard helps mitigate risks such as electrical short circuits, mold growth, or structural failure.
- Regulatory Adherence: Compliance with MS 655:08 is often a regulatory requirement. Manufacturers who adhere to this standard avoid potential legal issues and ensure that their products are approved for use in markets with strict quality and safety regulations.
- Consumer Trust: Products that consistently perform well, even in challenging environments, help build consumer confidence. Water resistance testing assures customers that the products they purchase will withstand water exposure without compromising performance.
The MS 655:08 Testing Process
The water resistance testing process as per MS 655:08 involves several key steps:
- Sample Selection and Preparation: Test samples are selected according to the specifications of the material in question. The standard ensures that these samples are representative of the material’s typical use conditions.
- Controlled Water Exposure: Samples are subjected to water exposure under controlled conditions. This may involve immersion in water, exposure to water spray, or placement in a high-humidity chamber, depending on the intended use of the material.
- Assessment of Effects: After exposure, the samples are closely examined for signs of water-induced damage, such as warping, cracking, swelling, or loss of mechanical strength. MS 655:08 provides detailed guidelines on how these effects should be measured and interpreted.
- Reporting: The final step involves compiling a comprehensive report detailing the test conditions, the observed effects on the material, and whether the material meets the water resistance criteria outlined in the standard. This report is crucial for determining the material’s suitability for its intended application.
Why Choose MS 655:08 for Water Resistance Testing?
Choosing to test materials according to the MS 655:08 standard offers several advantages:
Standardization: By following a recognized standard, manufacturers can ensure consistency across different batches of materials and across various products.
Reliability: The detailed procedures outlined in MS 655:08 ensure that the results of water resistance tests are accurate and reliable, providing confidence in the material’s performance.
Market Access: Adherence to MS 655:08 can be a key factor in gaining access to markets where compliance with international standards is mandatory.
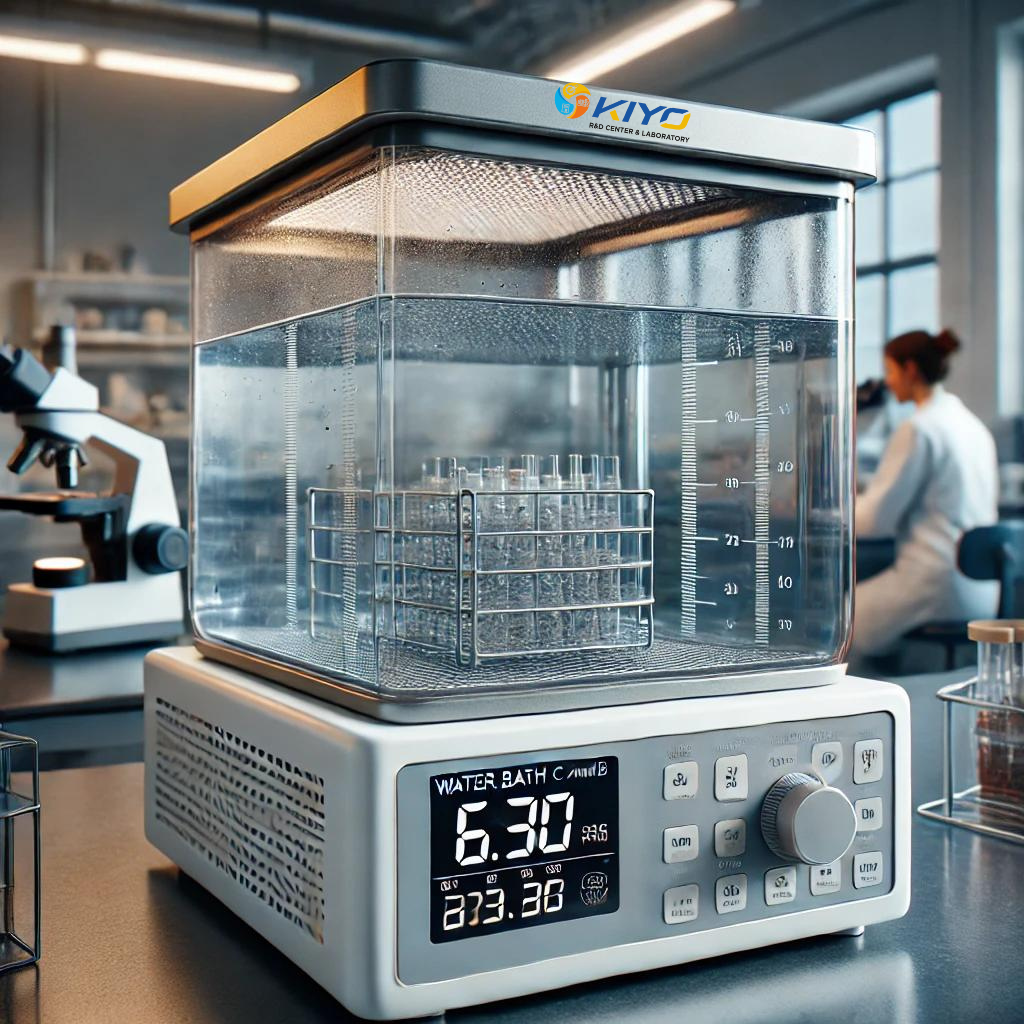

Conclusion
- Water resistance testing as per MS 655:08 is essential for ensuring that materials can withstand exposure to water without compromising their performance. This testing is not only about meeting regulatory requirements but also about guaranteeing the durability, safety, and reliability of products in real-world conditions. At Kiyo R&D Center & Laboratory, we offer comprehensive water resistance testing services that adhere to the MS 655:08 standard. Our expert team is dedicated to providing accurate, reliable results that help you bring high-quality, durable products to market. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist with your water resistance testing needs.